SAR-2021-020-LH
\newpage
Sample size for the verification of possible Interleukin-6 circadian rhythm in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficient patients
Document version
| Version | Alterations |
|---|---|
| 01 | Initial version |
| 02 | Added detectable effect for a given sample size |
Abbreviations
- BMI: body mass index
- CI: confidence interval
- d: Cohen’s D effect size
- IQR: interquartile range
- SD: standard deviation
Context
Objectives
Determine the sample size to detect the difference of the daily range of Interleukin-6 blood levels between Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficient and healthy patients.
Hypotheses
The circadian rhythm in patients induces a detectable amplitude between peak and lower daily IL6 levels. The average IL6 daily amplitudes differ between Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficient and healthy patients.
Data
Raw data
A unique study ID will be created for each participant to allow tracking of consecutive IL6 blood level measurements. IL6 data of each participant will be collected at three different times per day. Each datum will have its respective date and time of specimen collection recorded. Participant demographic characteristics to be collected are the group to with they belong (AAT-deficient or healthy), the date of birth, sex and BMI at the date of inclusion.
After the cleaning process the raw data will include 13 variables. Table 1 shows the structure of the raw dataset.
| id | group | sex | dob | bmi | date | il6_time1 | il6_measure1 | il6_time2 | il6_measure2 | il6_time3 | il6_measure3 | outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||
| … | ||||||||||||
| N |
Table: Table 1 Raw dataset structure.
Analytical dataset
Age at inclusion will be computed between the date of birth and the date of the first specimen collection.
For each patient the peak level and the lower level of IL6 measurements will be calculated. The peak level (respectively, lower level) of each patient’s IL6 will be calculated as the average of all peak level (respectively, lower level) measurements. The amplitude of each patient’s IL6 blood level will be calculated as the difference between peak level and lower level.
All variables in the analytical set will be labeled according to the raw data provided and values were labeled according to the data dictionary for the preparation of production-quality results tables and figures.
Study parameters
Study design
Cross-sectional.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
N/A
Exposures
Patients with Antitrypsin deficiency will be compared to controls.
Outcomes
Specification of outcome measures (Zarin, 2011):
- (Domain) Circadian rythm
- (Specific measurement) Amplitude of IL6 blood level
- (Specific metric) End value
- (Method of aggregation) Average
Primary outcome
The primary outcome for the detection of a circadian rhythm will be defined as the amplitude of the IL6 blood level which will be calculated as the difference between the peak level and the lower level of daily measurements.
The secondary outcome will be defined as the the difference between the average IL6 daily amplitude between healthy and AAT-deficient patients.
Covariates
No covariates will be considered for the sample size calculation. Age, sex and BMI will be used to adjust the estimates of the primary and secondary outcomes. Both raw and adjusted estimates will be computed.
Statistical methods
Statistical analyses
Descriptive analyses
N/A
Inferential analyses
N/A
Statistical modeling
N/A
Missing data
No missing data imputation will be performed. All evaluations will be performed as complete case analyses.
Significance and Confidence Intervals
All analyses will be performed using the significance level of 5%. All significance hypothesis tests and confidence intervals computed will be two-tailed.
Study size and Power
This sample size calculation assumes the exposed and control groups will be balanced in equal sizes.
We will consider three possible scenarios that the main researcher could choose from, all using Cohen’s d relative effect size (Cohen, 1988). This is a relative metric, accounting for both the mean and SD of the observed clinical measurements, thus simplifying the interpretation of the clinical effect into a single figure. A large effect requires less samples to be detected than a small one, but is typically considered as rarer effect.
Here we consider the small effect size defined as Cohen’s d = 0.2, the medium as d = 0.5 and the large effect size as d = 0.8.
Large effect size
With sample size of 26 per group a t test would be able to detect an effect size of d = 0.8 with 80% power at a 5% significance level (alpha). For this effect size the total study size would require the inclusion of 52 participants.
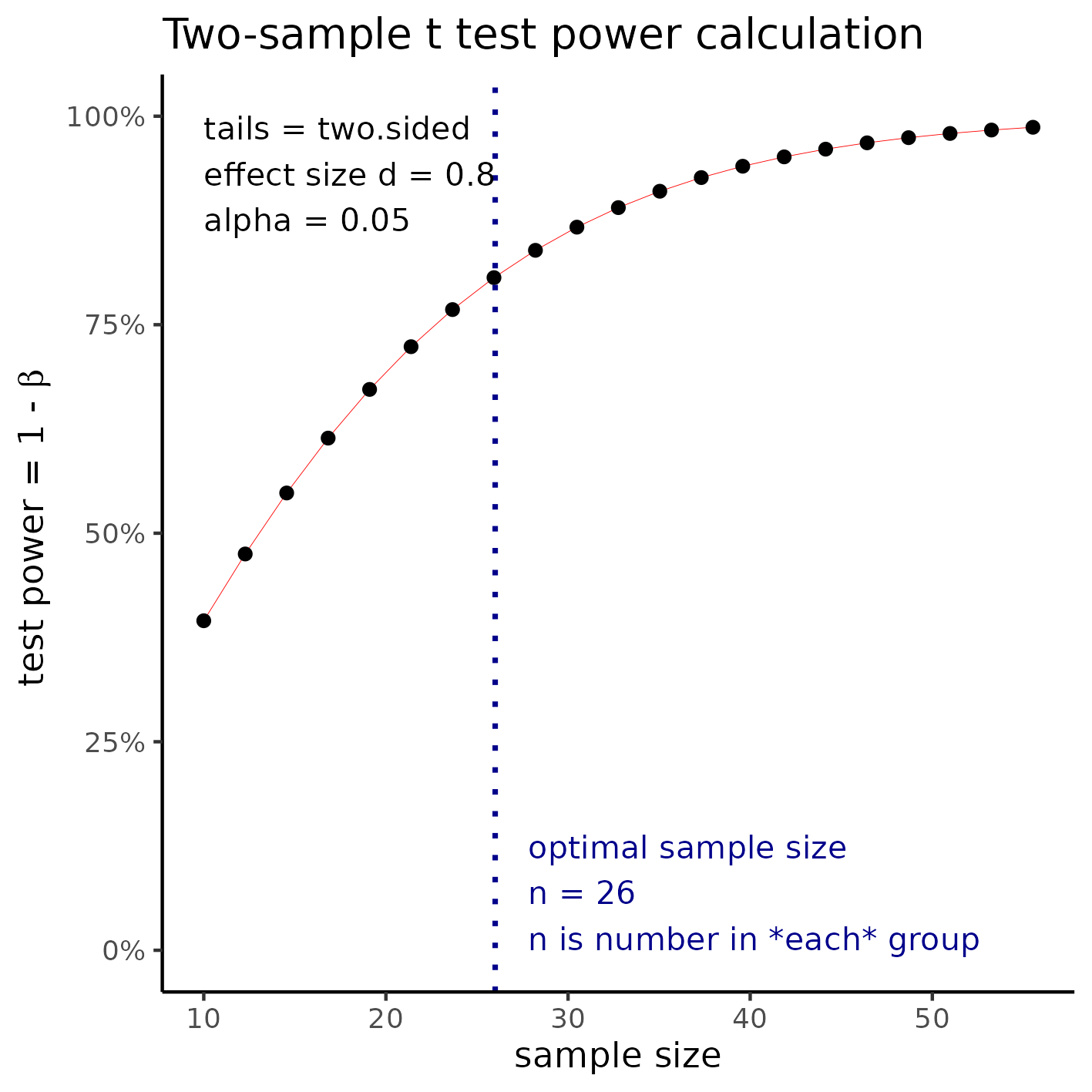
**Figure 1** Sample size required to detect a large effect size.
Medium effect size
With sample size of 64 per group a t test would be able to detect an effect size of d = 0.5 with 80% power at a 5% significance level (alpha). For this effect size the total study size would require the inclusion of 128 participants.
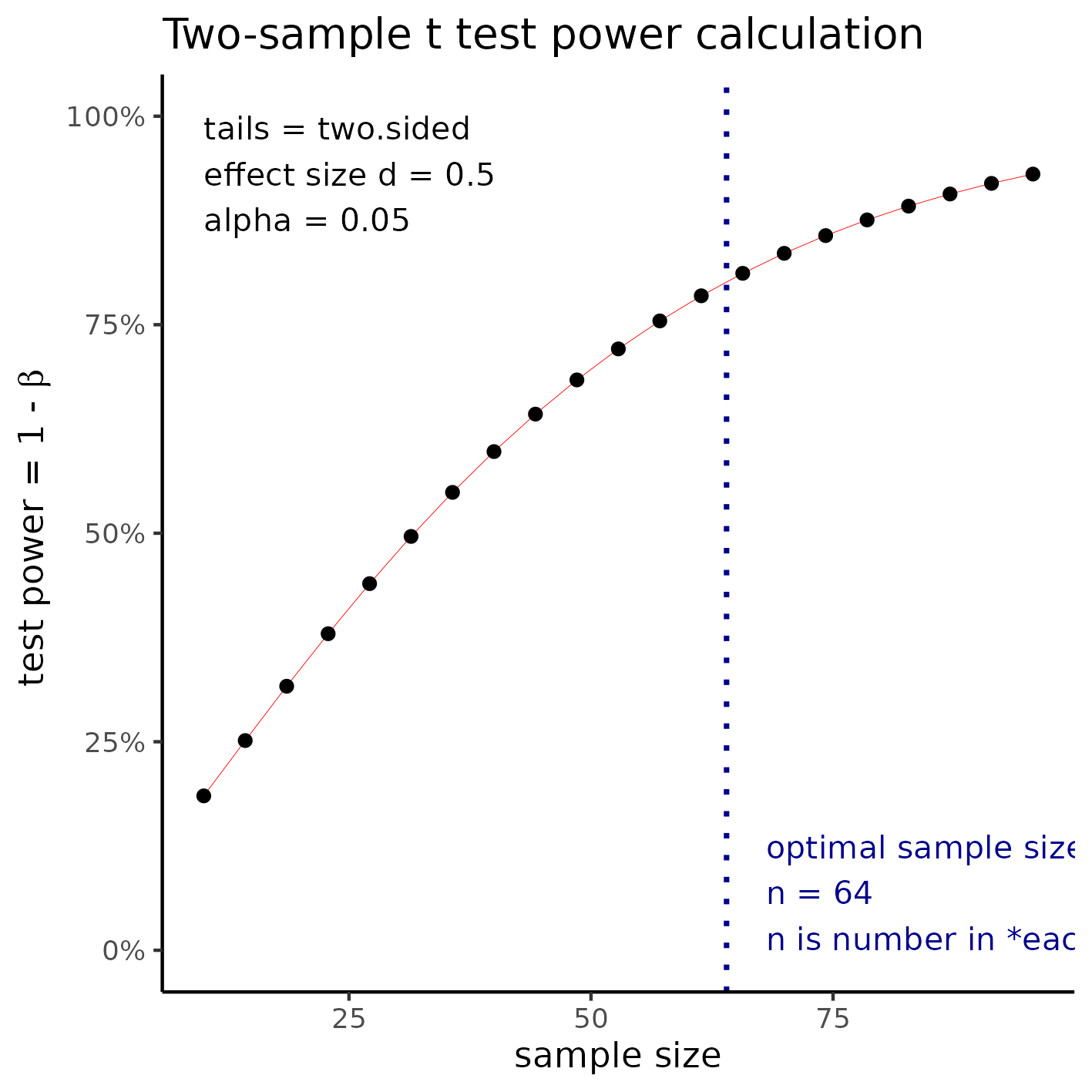
**Figure 2** Sample size for a medium effect size.
Small effect size
With sample size of 394 per group a t test would be able to detect an effect size of d = 0.2 with 80% power at a 5% significance level (alpha). For this effect size the total study size would require the inclusion of 788 participants.
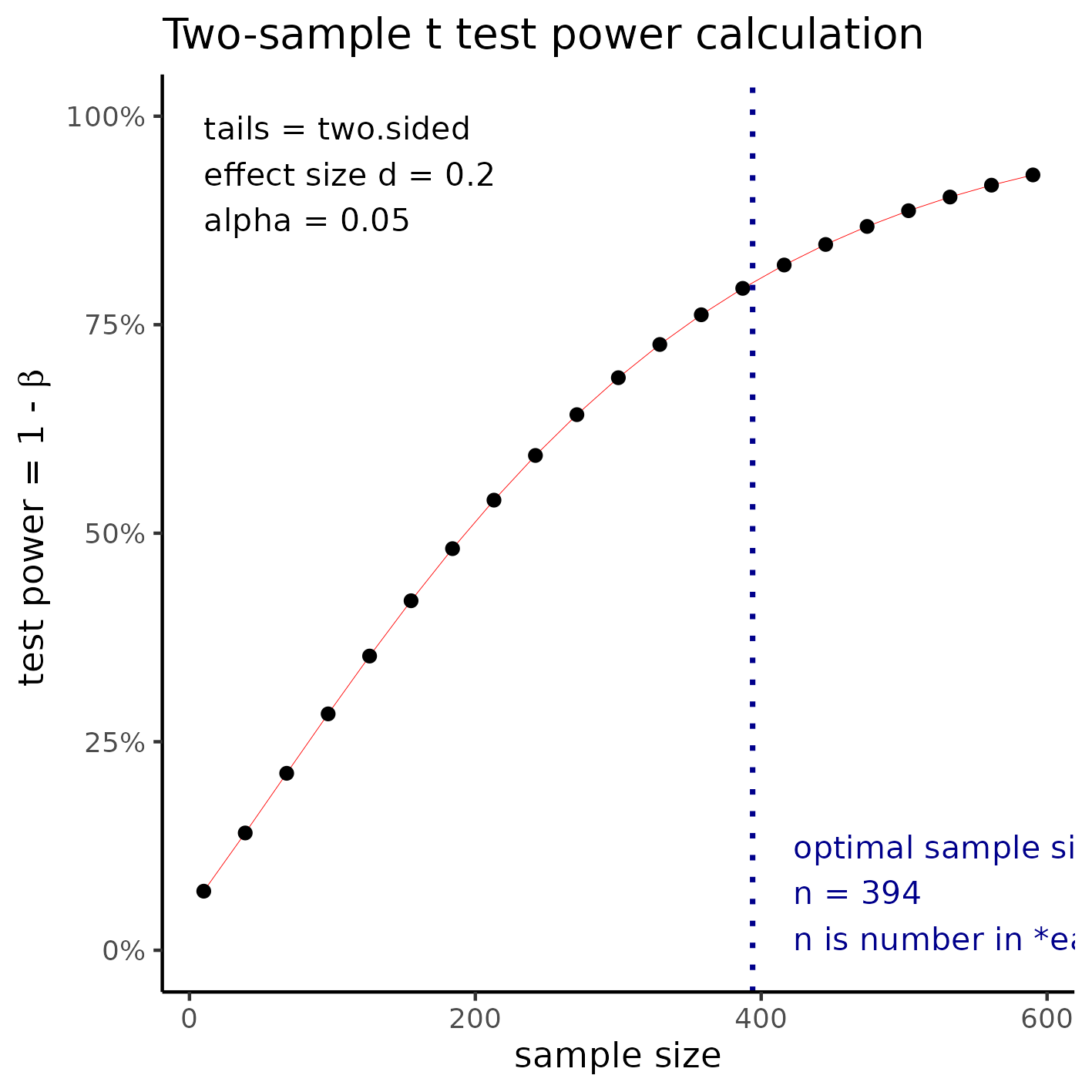
**Figure 3** Sample size required to detect a small effect size.
Effect size for a given sample size
If the maximum sample size feasible is N = 10 (divided into two groups of 5), then the minimum effect size that could be detected by this study would be d = 2.02.
This effect can be interpreted as the average amplitude (difference between peak value and low value) being twice as large as the SD for a t test to detect it.
Statistical packages
This analysis will be performed using statistical software R version 4.2.1.
Observations and limitations
Direction of the difference
The AAT deficient patient IL6 blood levels may be hypothesized to be lower (higher) than the levels observed healthy patients. If this hypothesis holds, a left tailed (right tailed) test will have more statistical power to detect significant differences than a two-tailed test. If there is support in the literature for an educated guess on the direction of the difference this could improve the chance of having significant p-values in the final analysis, at the risk of not detecting a difference in the other direction.
For example, if the hypothesis is specified in the left direction (group of interest has lower levels of IL6 than the healthy group) and the actual observed levels indicate that the group of interest has higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers, then the actual difference will likely not be significant in the study. It is recommended that such decision be made with caution.
References
- SAR-2021-020-LH-v01 – Sample size for the verification of possible Interleukin-6 circadian rhythm in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficient patients
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd Ed.). New York: Routledge.
- Zarin DA, et al. The ClinicalTrials.gov results database – update and key issues. N Engl J Med 2011;364:852-60 (https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa1012065).
- Gamble C, et al. Guidelines for the Content of Statistical Analysis Plans in Clinical Trials. JAMA. 2017;318(23):2337–2343 (https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.18556).
Appendix
This document was elaborated following recommendations on the structure for Statistical Analysis Plans (Gamble, 2017) for better transparency and clarity.
Availability
All documents from this consultation were included in the consultant’s Portfolio.
The portfolio is available at: